Enhancing Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability Through Technology
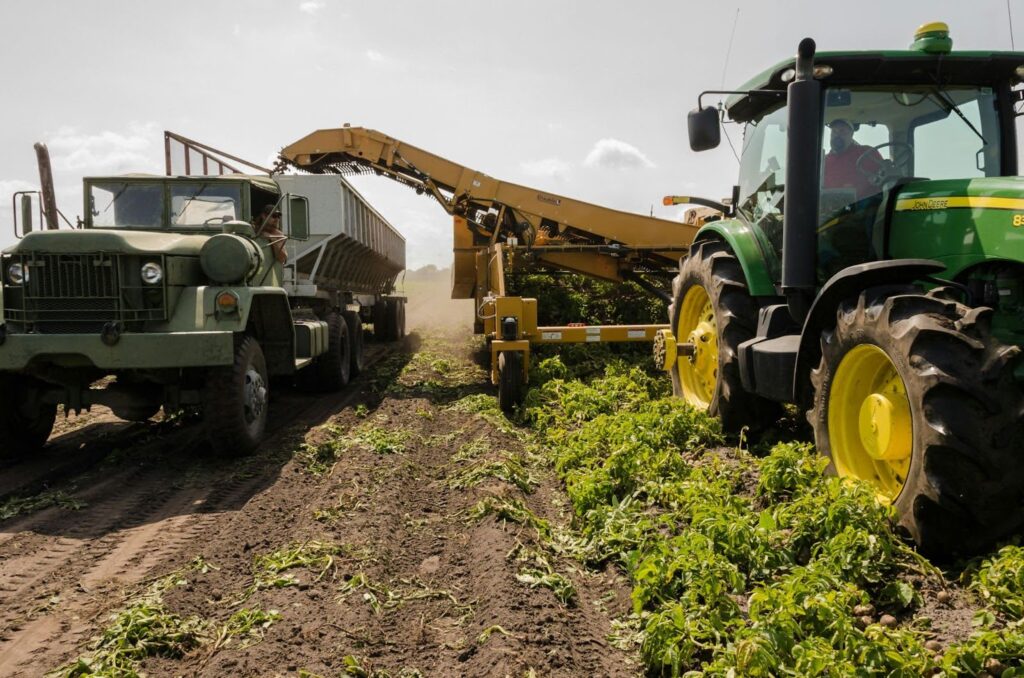

The agricultural technology market, often referred to as AgTech, is growing. By 2027, it will become a $30 billion industry. Innovators and inventors have been addressing longstanding issues within the agricultural industry and finding innovative ways to streamline production and protect crops. But AgTech is more than just automating agricultural processes; it also helps lessen the environmental impact of large-scale agricultural operations. This guide will examine trends and innovations in the modern AgTech landscape and help you find the tech to make your life easier.
Understanding Tech’s Role in Modern Agriculture
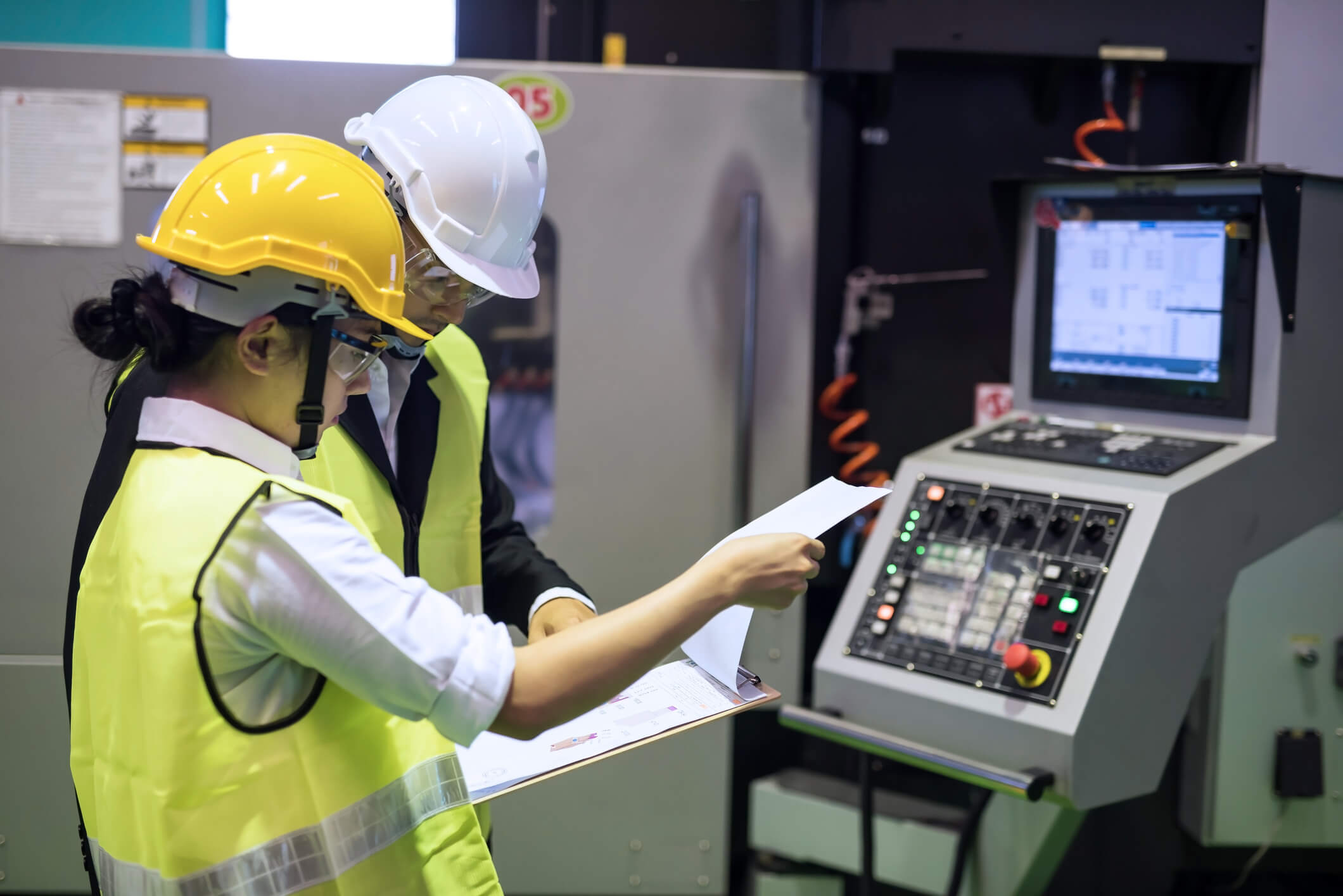
The integration of technology into agriculture has revolutionized the way we approach farming, from small-scale operations to large agricultural corporations. As global demand for food grows, AgTech innovators are finding new ways to streamline production and enhance efficiency.
New technologies like AI, IoT, and drone monitoring make everyday agricultural processes like planting, weeding, and harvesting easier. Powerful and sleek computers embedded within the machinery allow them unprecedented processing power and durability. These tools provide farmers with real-time data on soil moisture levels, crop health, and more, enabling informed decision-making that was previously impossible. Combining new technologies with traditional farming practices takes the guesswork out of agriculture.
Inventors and innovators have also turned their attention to sustainable agriculture practices. Large-scale agricultural operations can utilize renewable energy sources and significantly reduce food waste by utilizing sustainable AgTech.
Today’s Trends in Agriculture Technology
While the AgTech sector is rapidly evolving, these are the three main areas of advancement right now. AgTech innovators have focused on precision agriculture, sustainability, and automation.
Making Precision Agriculture Work for You
Precision agriculture is a modern strategy that utilizes technology to monitor and optimize various aspects of agriculture. Precision agriculture uses data analytics, GPS, and sensor technology to gain real-time data on individual fields and crops. These tools allow you to view your field conditions’ granular data and make decisions based on facts instead of educated guesses. By analyzing the data you receive from soil sensors and satellite imagery, you can give your crops the personalized attention and care they need, thus increasing yield and efficiency.
Embracing Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Sustainable agriculture technologies focus on preserving resources and minimizing chemical use, promoting biodiversity and soil health. Precision agriculture technology often informs eco-conscious decisions, such as water conservation in crop fields and lowered chemical usage. Moreover, technology facilitates the adaptation of regional and industry best management practices (BMPs) by providing data-driven insights into sustainable farming methods. Agriculture managers can learn more specific techniques from each other and foster a community of learning and shared responsibility to the environment.
Automating Daily Operations
In recent years, there has been a boom in agricultural robotics. Large-scale agriculture operations can now employ robots to harvest, weed, fertilize, and more. The goal of agricultural robots is to automate the time-consuming, repetitive tasks that could previously only be done by humans. With the AgTech advancements we have seen in recent years, these robots are more sophisticated than ever before.
For example, the Harvest CROO autonomous harvester utilizes an AI- and LIDAR-powered visual system to scan every fruit and vegetable for ripeness, disease, and more. Similarly, Polly the Pollinating Robot by Arugga has a sophisticated AI algorithm for determining what flowers are ready for pollination and automatically releases pollen to fertilize the buds. Instead of relying on pollinators like bees and insects, agricultural managers can ensure that every viable flower gets fertilized and turned into fruit. This can increase crop yield and nearly eliminate waste within
Agricultural robotics give you the power to control more aspects of the production process than ever before. Some are even equipped with built-in touchscreen computers to make maintenance and navigation easy. While the startup costs for these robots can be hefty, their utility over time will make it worth it.
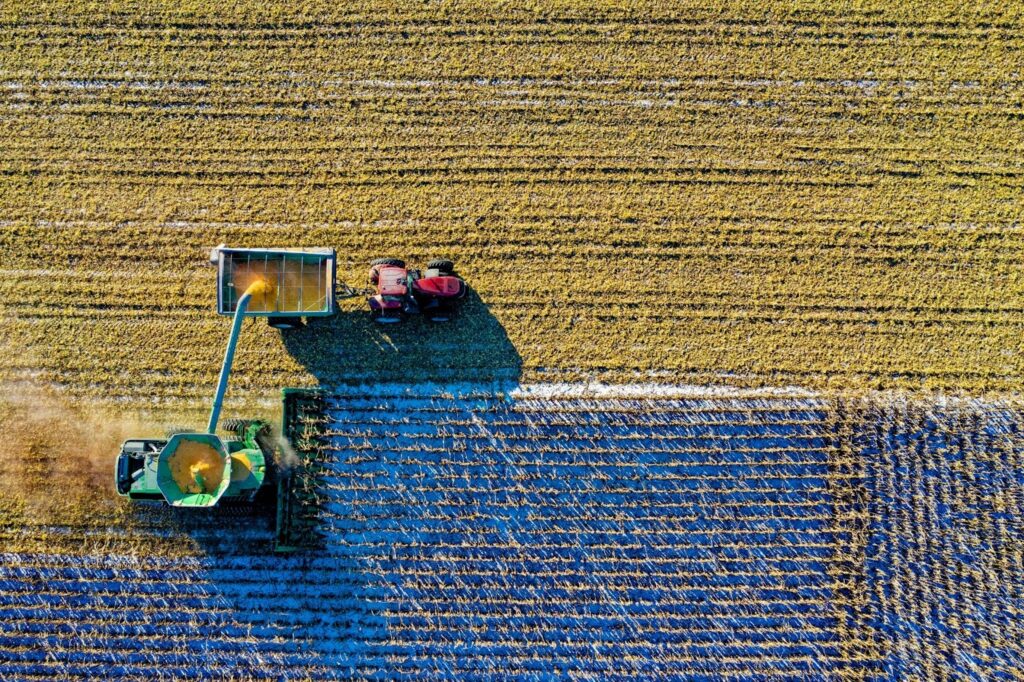

Innovations in Crop Monitoring and Management
One of the most impactful applications of modern AgTech is crop monitoring. You can manage your resources more efficiently and spot trouble before it starts. Here’s how.
Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing for Crop Health
Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies have revolutionized how we monitor the health and progress of large-scale farms. Satellites capture images of the Earth from above, tracking weather patterns, land use, and crop growth. They are especially useful for monitoring row crops or nitrogen in the soil, allowing you to monitor your fields’ vigor and vitality. Getting a bird’ s-eye view of your farm saves you the time of manually checking the health of your fields and frees up labor hours to dedicate to other tasks.
Companies like Planet and FarmQA provide satellite imaging services to agricultural operations. By employing algorithms that analyze this data, these services can accurately predict crop yields and identify areas that require attention. This way, you can stop problems before they start and more accurately predict issues based on that year’s rainfall or other weather conditions. Integrating satellite data with on-the-ground management strategies ensures timely and precisely targeted interventions, optimizing crop health.
Sensor-Based Soil and Crop Monitoring
You’re probably familiar with basic, consumer-grade soil sensors — monitors with a small rod you can stick in the ground and get a nutrient reading from. Large-scale soil sensors, though, track soil moisture and quality throughout an entire field and provide real-time updates. Not only do these high-tech sensors give you information about your soil, but they can also integrate with other technologies to give you advice about soil care.
There are a few different kinds of specialty soil sensors —some utilize underground radio technology to get deep-earth nutrient and moisture information. In contrast, others monitor soil moisture and vitality with advanced satellite technology. These sensors often utilize IoT technology to communicate with other sensors around your farm. This intercommunication with other devices allows you to view real-time data for your farm at a glance.
These sensors can be most impactful when used to inform your irrigation system. You can utilize the data from your soil sensors to see which areas need more and less water and tailor your system to provide that. This will conserve water usage, prevent waste, and ensure that all crops have their specific needs met.
Agriculture Management Software Integrations
These sophisticated platforms integrate various data sources, including satellite imagery, sensor data, and weather forecasts, into a unified system that offers a comprehensive overview of your operations. Some programs also utilize AI and sophisticated machine learning algorithms to help monitor your crops and suggest solutions if problems arise.
Programs such as Farmbrite, Chetu, and AgWorld are promising players in the AgTech management world. Take your time when deciding on management software; do not be afraid to meet with multiple representatives and see who can provide the best software solutions for your business. A sound software system will be intuitive, all-encompassing, and, above all else, helpful. Talk to representatives about the technology and devices you already use, as most management software can integrate quickly and easily with your existing tech. When purchasing a management system, also look into purchasing a rugged tablet to accompany it — this way, you’ll have the data at your fingertips.
Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Agriculture
The agricultural industry uses over 70% of the world’s water. Modern AgTech professionals are finding ways to reduce this number and conserve water whenever possible.
Smart Irrigation Systems
AI-powered smart irrigation systems utilize data gathered from satellite imaging, local weather data, and soil sensors to water crops on a customized schedule. The irrigation AI is trained to analyze this data and learn from historical patterns. This prevents water waste and underwatering, leading to happier crops and a better environmental impact.
Some companies at the forefront of smart irrigation are HydroPoint and Lumo, but the field is drawing a lot of attention. Many new smart irrigation startups are finding the best ways to conserve water and streamline your schedule.
Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics are soil-less farming techniques that complement traditional agriculture. Aquaponics combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants without soil) in a closed-loop system. The waste produced by the fish provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, while the plants help purify the water, which recirculates back to the fish tanks. Hydroponics, on the other hand, involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution, eliminating the need for soil and significantly reducing water usage compared to conventional farming methods.
You do not need to convert your entire operations to a fully hydroponic farm; you can integrate these technologies into your existing structure. For example, greenhouses can house hydroponic systems, allowing for year-round crop production with minimal water use. This could benefit from the addition of a wall-mounted computer to monitor water quality and fish health.
You may dedicate a building to aquaponics, raising fish and plants in the same environment to diversify your production. Both systems are highly water-efficient, reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and can be implemented in areas with poor soil quality or limited water resources.
Challenges and Solutions for Adopting New AgTech
While AgTech can bring you many benefits, it is not without drawbacks. Many AgTech innovations are pricey, have limited capabilities, or are not user-friendly. The industry is in a state of rapid change, which can reflect the challenges you face trying to access new technology.

Startup Costs
Depending on the size of your operation and the kind of technology you need, your upgrades might be costly. Advanced systems like precision irrigation, robotic harvesters, and sensor networks come with significant investment costs that smaller agriculture businesses may struggle to pay. Moreover, if any of these systems break or malfunction, the repair cost could be steep.
But you don’t necessarily need to find an angel investor or launch a crowdfunding campaign to afford these upgrades. Myriad subsidies, grants, and loans are designed specifically for the agricultural sector. The federal government also offers subsidies for farms exploring sustainable agriculture practices.
Connectivity and Infrastructure Limitations
One of the primary challenges in rural areas is the lack of reliable internet access and technological infrastructure, which is essential for the optimal functioning of many AgTech solutions. This connectivity gap can hinder real-time data collection, cloud-based analytics, and remote monitoring systems. While you may not be able to petition a company to build a cell tower closer to your farm, you may decide to utilize lower-tech methods until connectivity becomes more consistent in your area.
Learning Your Tech
Finally, your tech is only worth what you can do with it. Learning not only how to operate your AgTech but also how to analyze the data it collects can be a time-consuming process. Many technology providers offer comprehensive training programs and user support to facilitate this learning process. Take advantage of the lessons and resources providers give you, and do not hesitate to seek additional education online or from specialty providers. A sophisticated software program can also make data analysis more manageable, giving you digestible pieces of information alongside AI-powered advice.
Building A Tech-Savvy Agriculture Community
Upgrading your tech is easier if you have others to discuss it with. Local meetups, demonstration farms, and online forums offer valuable platforms for AgTech users to exchange insights, learn from one another’s experiences, and see technology in action. Agricultural extension programs play a crucial role by providing tailored education to local farmers, acting as a bridge between research and practical application. These efforts are complemented by digital spaces such as social media platforms and online courses, which allow for broader, more inclusive discussions on the latest in AgTech, breaking down geographical barriers and enabling a global exchange of ideas.
To find other agricultural workers interested in new technologies, all you have to do is reach out. The innovations in modern agriculture are staggering but promise to lead to a more sustainable and productive future.

Resources for Farmers Looking To Update Their Tech
Whether you need help with funding, learning new tech, or buying new equipment, here are some resources we suggest.
Funding and Grants for Adopting Agricultural Tech
- Local Agriculture Market Program (LAMP): This program offers $133 million in grant funding to expand and strengthen local and regional food systems and increase the availability of locally grown agricultural products. It includes the Farmers Market Promotion Program (FMPP), the Local Food Promotion Program (LFPP), and the Regional Food System Partnerships (RFSP).
- Rural Innovation Stronger Economy (RISE) Program: This program supports community-driven projects to create high-wage jobs and new businesses in underserved rural communities. It encourages regional, innovation-driven approaches to economic development. These jobs can include tech specialists for agricultural innovations, allowing you to hire experienced workers for your machines.
- Urban Agriculture and Innovation Production (UAIP) Grants: These grants target projects that enhance urban, indoor, and innovative agricultural practices. Eligible projects may include community gardens, rooftop, indoor, and high-tech vertical technology farms. Priority is given to organizations with a proven capacity for meaningful community-focused work in urban agriculture.
- Rural and Agricultural Income & Savings from Renewable Energy (RAISE) Initiative: This initiative, a collaboration between the USDA and the Department of Energy (DOE), focuses on helping farmers reduce costs and increase income through underutilized renewable technologies such as smaller-scale wind projects. It leverages the Rural Energy for America Program (REAP) and includes funding from the Inflation Reduction Act.
- SDBII Farm Infrastructure & Precision Technology Grant: This grant offers two tracks for applicants: the Farm Infrastructure Improvement Grant and the Precision Technology Investment Grant. Both are designed to improve the competitiveness of southeastern dairies by providing funding for infrastructure improvements and the adoption of precision technology. Currently, it is only open to select states in the American Southeast.
Technology Suppliers for Popular Agricultural Technology
- Bee Vectoring Technology (BVT): An innovative company that has developed a unique system utilizing bees to deliver pesticides and other treatments directly to crops. This method benefits crops like strawberries, apples, and tomatoes, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional spraying methods.
- Teguar Corporation: Specializes in providing industrial and medical computer solutions, offering a range of rugged, waterproof, and durable computing devices designed for the demanding environments in agriculture and healthcare. Teguar is committed to delivering cutting-edge technology tailored to specific industry needs, ensuring reliability and performance in even the most challenging conditions.
- Farmers Edge: Offers advanced farm management software (FMS) solutions that enable farmers to make data-driven decisions for their operations. Their platform integrates real-time data monitoring of crops and livestock with predictive analytics to optimize resources, enhance productivity, and increase profitability.
- Smartbow: Provides livestock monitoring technology that includes ear-tag sensors capable of measuring various health indicators such as temperature, pulse, and location. This technology helps in early disease detection, improving herd health and efficiency in livestock management.
Educational Materials and Training for Farmers Looking to Learn
- Purdue University College of Agriculture offers a Precision Agriculture course that is 100% online and designed for agricultural practitioners. This 12-week non-credit course covers the science of site-specific farming and includes over 90 video lessons and additional educational materials. It’s ideal for those seeking flexibility, as participants can access content anytime that suits their schedule.
- Michigan State University’s Institute of Agricultural Technology delivers educational programs aimed at developing career-ready graduates through practical learning in agricultural, environmental, and applied technologies. The institute has been foundational since 1894 and offers a mix of certificate programs to cater to various interests within the agTech field.
- Rodale Institute’s Farmer Training (RIFT) program provides an immersive experience in organic agriculture. It combines classroom instruction with farm visits and hands-on training to equip aspiring farmers with the knowledge and experience necessary to embark on a career in regenerative organic agriculture. The program highlights include eligibility for accessible housing, access to Rodale workshops, and a weekly stipend.
- The University of Northwestern Ohio offers programs in Agricultural Equipment Technology. These programs focus on the technology behind modern agricultural equipment, with coursework covering electronics, diesel engine diagnosis and repair, hydraulics, and more. Training includes hands-on experience with agricultural training aids from major manufacturers, preparing students for careers in dealerships, corporate, and family farms.