The Differences Between a PLC and an Industrial Computer

With automation becoming increasingly critical in industrial settings, it is important to choose the right advancements for your specific use case. For people like manufacturing professionals, automation engineers, and IT specialists, understanding the nuances of PLCs and industrial computers is a critical part of maintaining a competitive edge.
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
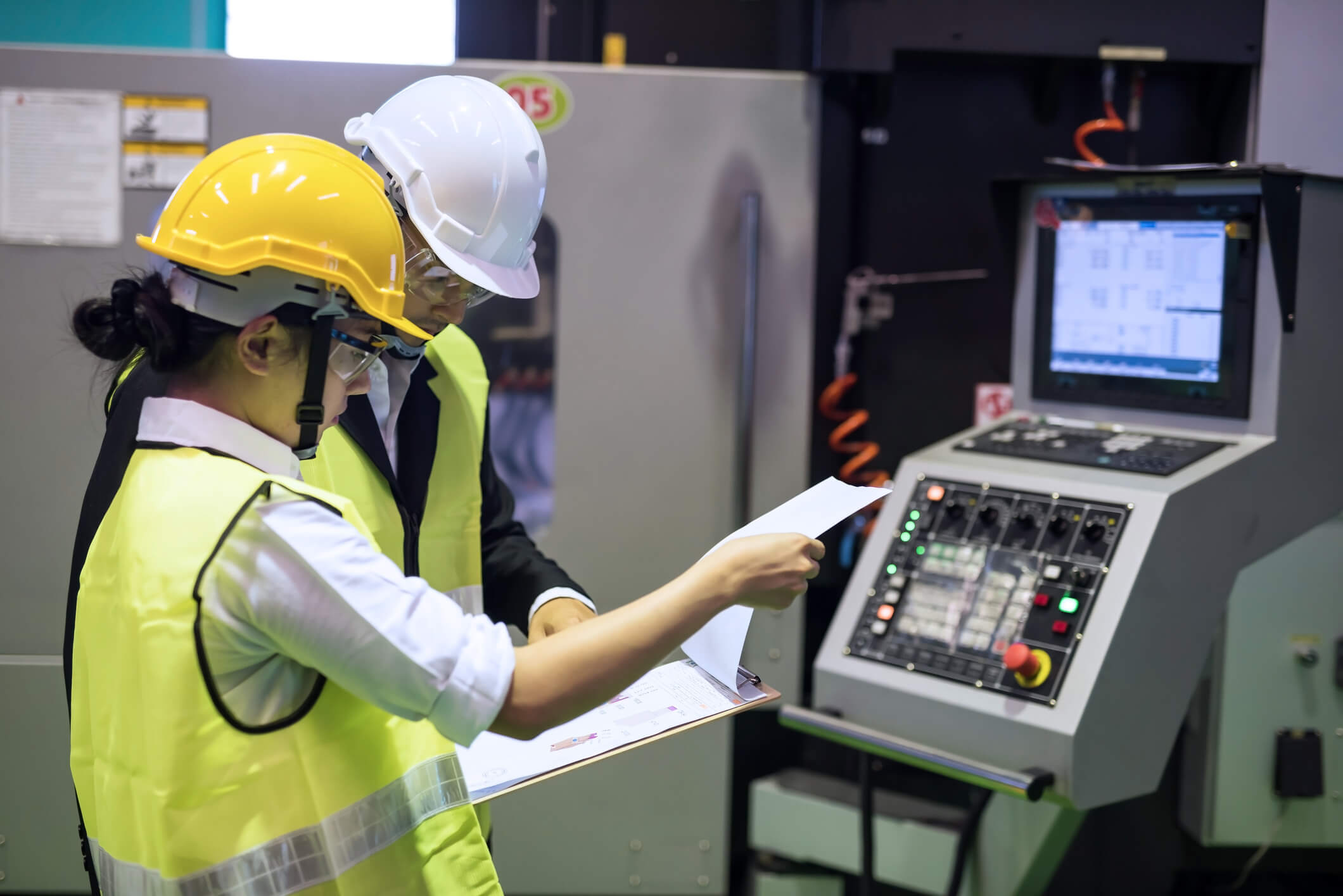
A PLC is an industrial digital computer used in the automation of electromechanical processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines, amusement rides, or lighting fixtures. They read inputs from various sensors and devices, process the data, and control the state of outputs such as motors, valves, and other devices. Compared to general-purpose computers, PLCs are typically ruggedized, have much shorter scan times, and greater immunity to electrical noise. They are also designed to withstand harsh industrial environments and include extensive input/output (I/O) connectivity.
Advantages of PLCs
- Reliability and ruggedness
- Faster cycle times
- Better suited for high-temperature and high-noise environments
- Specialized input/output capabilities
Limitations of PLCs
- Less processing power compared to industrial computers
- Limited functionality outside industrial automation
- High hardware costs for complex systems
Industrial Computer
Industrial computers are designed to operate reliably in harsh usage environments such as strong vibrations, extreme temperatures, and wet or dusty conditions. These computers often support applications that require excellent processes & graphics performance, as well as diverse I/O (input/output) features. They can be used for data acquisition and control, networking, and complex computing operations in various manufacturing segments, from automotive to pharmaceuticals.

Advantages of Industrial Computers
- Handling more complex applications than PLCs
- Easier integration with IT systems
- Remote monitoring and control
- Cost-effective for large systems with high intensity computational operations
Limitations of Industrial Computers
- May require additional ruggedization or protection in harsh environments
- Potentially higher maintenance requirements
- Initial investment can be significantly higher when compared to PLCs
Comparison
To choose between a PLC and an industrial computer, manufacturing professionals must consider performance metrics, programming capabilities, as well as the systems’ flexibility and scalability.
Performance Metrics

When it comes to speed, PLCs often have the upper hand with their high-speed I/O, designed for extremely fast responses. However, industrial computers are typically equipped with more advanced processors, which allow for superior performance in handling complex control and monitoring tasks.
Programming Capabilities
PLCs are associated with ladder logic programming, which is tailored to the needs of industrial control. While highly intuitive and efficient for control applications, it presents a learning curve for those familiar with standard programming languages used with industrial computers, such as C++ or Java.
Industrial computers, on the other hand, offer a broader range of programming options, which can be more familiar to IT specialists. This includes the ability to run a wider variety of third-party software for data analysis, manufacturing execution systems (MES), and other business-related software.
Flexibility and Scalability
PLCs win in system flexibility within their narrow application scope. They can be easily reconfigured for different functions or adjusted to new sensor types and numbers. However, this comes at the cost of scalability, as PLC systems tend to be more challenging to expand beyond their original scope.
Industrial computers, though starting with higher complexity, offer a more flexible base for scaling up with the addition of more powerful hardware or software upgrades. Their ability to integrate with standard networking protocols and equipment also makes them more scalable when it comes to expanding the scope of applications.
Customization
Teguar offers a wide range of customization options such as IP ratings, touch screens, wireless connectivity, and more. Thus, making it easier to tailor an industrial computer to meet the exact needs of a particular application or environment.
Teguar Industrial Computer Offerings
It is not a matter of which technology is better; it is a matter of which technology is more suitable for the specific manufacturing operation. At Teguar, our team works closely with clients to understand the requirements of their unique applications and recommends suitable hardware that can optimize processes.

Our range of industrial computer offerings caters to the diverse needs of manufacturing professionals, with products that are resilient, high-performing, and fully customizable to ensure seamless integration into your production environment.
Product Overview
- Fanless Industrial Computers – Silent, dust-free, and durable
- Industrial Panel PCs – Compact, built-in screens for space-saving control solutions
- Waterproof Industrial PCs – IP-rated enclosures for wet or dusty manufacturing environments
- Rugged Industrial Tablets – Portable solutions for mobile control and monitoring
- Customizable Industrial Computers – Tailored to your exact application requirements

Why Choose Teguar?
- Expertise in industry-specific needs
- Rugged yet reliable design
- Customizable solutions for a perfect fit
- Accelerated time to market
- Dedicated technical support
Choosing between a PLC and an industrial computer is a decision that requires a deep understanding of the manufacturing processes, the level of automation required, and the scalability of the system. While PLCs are the traditional choice for robust control in discrete industrial processes, industrial computers are gaining a foothold due to their versatility, processing power, and network capabilities.
For complex operations that demand high processing power or need to be integrated into a larger system, industrial computers may be the better choice. Teguar’s expertise in industrial computer technology can guide manufacturing professionals to make the best choice for their unique requirements, ensuring that automation efforts are as efficient and productive as possible.
In the end, both technologies have their places in the manufacturing landscape. The key is to leverage their strengths for the greatest strategic advantage. Whether you’re upgrading an existing system or designing a new one, Teguar is ready to help you make the right decision.