What are the Benefits of Edge Computing?
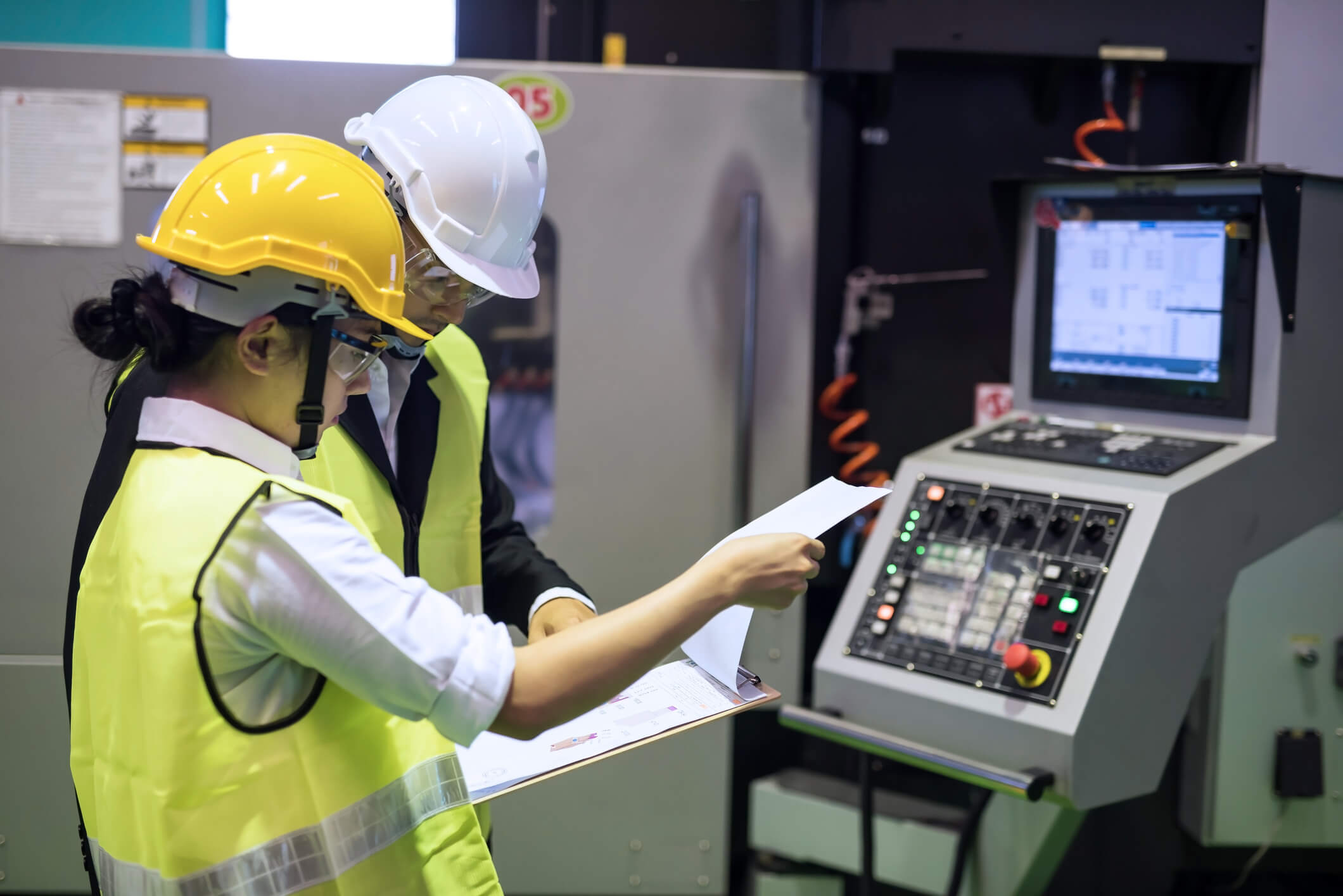
Edge computing moves data processing close to where the data is actually being collected. This means less data is processed in the cloud, and more on an edge computer or device. If you haven’t already read our introduction to edge computing, we suggest you start here: What is Edge Computing?
Below are three main benefits of edge computing, including faster speeds, greater system reliability and better information security. There are other benefits not addressed here, such as potential cost savings, by reducing your amount of cloud storage and bandwidth, and better scalability, as adding another facility won’t overload your network.

Edge Computing Makes Data Processing Faster
Localizing some of the data processing and storage allows your device to make decisions in milliseconds, or even nanoseconds, rather than several seconds. This is most important for applications where a millisecond can make a big difference, such as autonomous cars or drones. Let’s consider drones, for example. The idea of purchasing something online and receiving it by drone minutes later may be an everyday reality for millions within a few years.
Like the GPS in your car, the GPS in the drone will need to get information from the cloud, for constant updates on new construction zones, cell towers, and anything else that might get in its way. However, if a bird or baseball flies at it, the one second in latency between the drone and the cloud could result in costly hardware damage. Or worse, it could fall on someone and result in injury or death.
Before we fill the sky with autonomous drones, we need to know the drones are capable of making decisions in milliseconds. Having the processing power onboard is essential for lightning fast, unexpected decision making. The capability to make some decisions locally and in real time makes the device or system more reliable.

Edge Computing Increases Reliability
In the case of a drone or autonomous car, reliable network connection is important, but can’t always be expected. If the network connection is lost, or just slow, the vehicle needs to be able to make decisions on its own, even if that just means safely coming to a stop until network connection is restored. Edge computing gives the device or machine more control. It does not rely on super-fast network speeds for basic functionality.
Another example where the reliability of edge computing is very important is in food manufacturing. Sensors and measuring devices are placed along the manufacturing line to detect defects. In poultry processing, for example, a laser thermometer might be used to ensure the meat has reached the proper temperature. Within milliseconds, the decision can be made to remove the product from the production line, if it does not meet proper standards. This happens extremely quickly because the computing is being done in the plant, typically in the same room on a computer, or in the same building on a server. If instead, this data was sent to the cloud and computed elsewhere, the decision might take 2 seconds, rather than 200 milliseconds. This could result in contamination of other products, or 2 seconds of delay, which will add up over time.
Keeping some computing tasks close to the manufacturing plant or vehicle is beneficial. If the network connection is lost, or slow, your machine can still perform essential tasks. Later, less time sensitive data can be sent to the cloud, such as average temperature of the batch or number of rejects. Another benefit of distributing some of your data processing and storage, is that it can make your business more secure.

Edge Computing Increases Information Security
When he said “don’t put all your eggs in one basket,” Aesop probably wasn’t thinking about centralized networks and data centers, but his lesson applies here. Relying on one data center to process and store all your business data is risky. If that data center falls victim to a cyberattack, your entire operation could be shut down.
Whereas, if you decentralize your network, it’s very unlikely that a cybercriminal could steel or manipulate all of your data. If you are unfortunate enough to be the victim of a malware attack or data breach, at least only part of your operation will have been compromised. Having the ability to store and process data in multiple locations can give you redundancy that may save your operation when the unexpected occurs.
Edge computing can only make you more secure, if you use the right devices. Using a hardware-based security measure, like TPM, is a key requirement for computer hardware used for edge computing.
Read our next article, to learn about other computer hardware requirements for edge computing. Contact us to discuss your edge project, or request a demo of one of our edge computers.