What is an NPU? And what can I do with one?
A Neural Processing Unit (NPU) is a very low power chip, meant to operate consistently while drawing very little power. This makes it a highly efficient power saver when performing repetitive tasks. Most notably, it excels in Artificial Intelligence-based activity such as machine vision.
A computer’s GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) works together with the NPU to power these tasks, removing the burden from the CPU. It also allows operations to happen locally, instead of in the cloud. By offloading these specific computations to the NPU, the main CPU and GPU are freed up, reducing energy consumption and improving processing efficiency for AI-heavy tasks.
NPUs from Intel
Intel® offers its own proprietary NPU built-in to many of its processors, starting with its 14th Generation Meteor Lake, boasting up to 8x the power efficiency of the 13th Generation for AI-based workloads. They refer to the chip as an AI Boost, and the package deal as an AI PC. It is suitable for applications such as Stable Diffusion and AI chat bots.
This included NPU is a convenient and affordable solution that comes right out of the box with majority of the latest Intel processors.
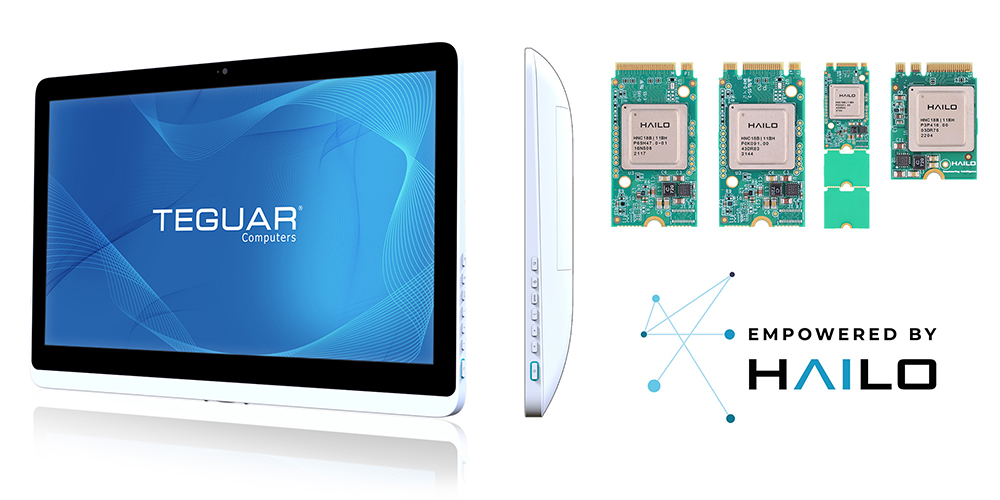

This all-in-one PC from Teguar is compatible with the NPUs from Hailo, empowering it to run higher powered AI tasks than with an Intel NPU.
NPUs from Hailo
Coming in at a few steps higher in power level are the NPU chips from Hailo. Though you can’t beat the availability of Intel’s built in NPU, the average chip from Hailo is still affordable as well. They refer to their chips as AI Accelerators. Hailo is advertised to be used for smart driving applications, though their NPUs also excel at repetitive automated tasks such as anomaly detection in manufacturing.
Consider one of these if you are running a more demanding program that requires a higher power draw.
What is an NPU best used for?
NPUs are proficient at handling image processing tasks like sorting and object tracking, making them perfect for applications such as automated assembly lines and security systems. They handle real-time tasks such as speech recognition, facial recognition, and other sensory data processing, often without needing a connection to the cloud.
NPUs are commonly used in edge devices where low latency and power efficiency are essential. For AI workloads that must operate within power-constrained environments — such as mobile devices or drones — NPUs are ideal, since they are optimized for that low power consumption.
Do I need an NPU?
For consumer use or smaller scale projects, a strong GPU may be a better choice. A graphics card is necessary for running large AI models and for “teaching” or creating them. The NPU is best for running the applications and using existing models. In other words, a GPU is best for creating AI models, while NPU is best for efficiently running them once created. As a result, if you have a strong GPU and power usage is not a concern, you may be better off sticking to the graphics card alone.

For industrial applications, an NPU is absolutely recommended; they’re the most efficient solution for handling large scale AI tasks across many devices. This AI-optimized card will handle the workload locally and with low power consumption.
A solid NPU is also likely to be more cost-effective than a high-powered GPU. Therefore, if you won’t be creating or training any new AI models yourself, we recommend you explore some of the NPU chips above — from Intel and Hailo — for affordable solutions.
NPUs from Teguar
For a computer with Intel’s AI Boost NPU, look forward to the launch of our Clarion All-in-One Medical PC next year. Explore our computers that are compatible with Hailo’s AI Accelerators here.
Or, looking for a box PC that can handle these and other powerful chips like a strong graphics card? Look no further than our TB-7145-MVS Rugged AI Platform PC with space for up to three PCIe cards.
If you have any other questions about NPU and how to use them in your Teguar computer, get in touch with us today.