How will 5G Impact Healthcare and Industry 4.0?

What is 5G?
5G stands for 5th Generation and it is the next generation of wireless communication. The standards for 5G are set by the International Telecommunications Union. Cellular network providers T-Mobile, AT&T, Verizon and others have already begun deploying 5G across the US and other countries. These are mixed with a couple versions of 5G technology called Sub 6 and mmWave depending on the carriers.
GSMA (Global System for Mobile Communications Association), a leading source for research and insights in the mobile industry, published a 288 page guide to 5G in April 2019, here are a few main takeaways:
- 5G will be 10-100x faster than 4G.
- 5G networks will “cover nearly 40% of the global population by 2025.”
- 5G is based on the same technology as 4G (unlike 2G and 3G), so 4G and 5G will coexist for a long time.
- “5G will create $2.2 trillion of economic value by 2034.”
What will 5G do?
The development of 5G was driven by the rapidly growing consumer demand for connected devices. It helps to take a look back at what 1G – 4G accomplished.
- 1G – Analog Voice Support (1980s)
- 2G – Digital Voice Support, data speeds of up to 64 Kbps (1990s)
- 3G – Cellular Data, data speeds up to 2 Mbps (2000s)
- 4G – Improved Cellular Data, data speeds around 20 Mbps (2010s)
- 5G – Improved Cellular Data, data speeds around 400 Mbps (2020s)
(read more about 1G – 5G)
With 5G, more devices can be connected, with more reliability and speed. 5G has a wider bandwidth than 4G, so even in a crowded areas, your smartphone will have fast upload and download speeds. This also means smart homes and smart factories can have dozens, hundreds, or even thousands, of enabled devices, without slowing down network connection.
5G will lead the way to new technologies that we have never seen before, as well as greatly improve technologies such as cloud computing, smart homes, virtual reality, industrial automation and much more.
5G and Industry 4.0 / IIoT
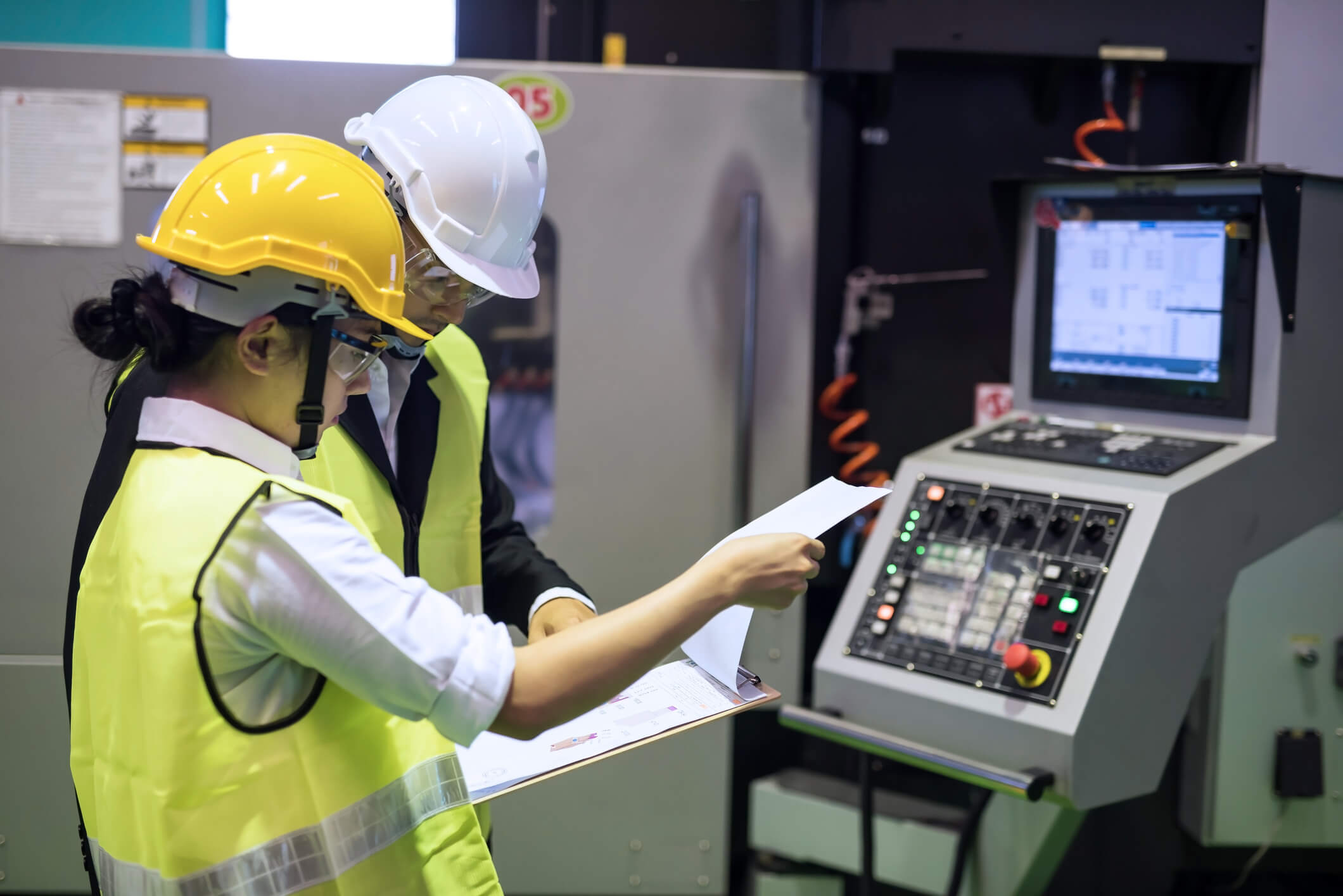
 The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), also called Industry 4.0 or the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to the network of connected devices in industrial settings. Computers, cameras, sensors, and machines are all examples of IIoT devices. These devices collect, analyze, and share data in real time, to enable processes like machine vision, predictive maintenance, and asset tracking. WiFi, Bluetooth, and 4G/LTE have made it possible to connect virtually any device in a factory or warehouse setting. 5G is here to take the IIoT to the next level.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), also called Industry 4.0 or the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to the network of connected devices in industrial settings. Computers, cameras, sensors, and machines are all examples of IIoT devices. These devices collect, analyze, and share data in real time, to enable processes like machine vision, predictive maintenance, and asset tracking. WiFi, Bluetooth, and 4G/LTE have made it possible to connect virtually any device in a factory or warehouse setting. 5G is here to take the IIoT to the next level.
With its wider bandwidth and extremely low latency, 5G allows for more connected devices, which collect massive amounts of data and process it very quickly. On manufacturing lines, Machine to Machine (M2M) communication will greatly improve, allowing for more rapid prototyping, easier product customization, and better predictive maintenance. Connecting more devices also gives way to end-to-end supply chain visibility. With better supply chain tracking, AI can predict shortages and changes in demand, and adjust production speeds accordingly.
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR and VR) will also greatly improve, thanks to 5G. VR can be used to remotely monitor or repair machines. AR can be used to see live machine data or even see “inside” a machine using CAD drawings and 3D renderings.
As with the consumer market, the industrial sector will not realize the full benefits of 5G immediately. We know that current processes and technologies will improve and expand. We can predict a future in which autonomous factories, self-driving vehicles and drones, and industry automation become the new norm.
5G and Healthcare
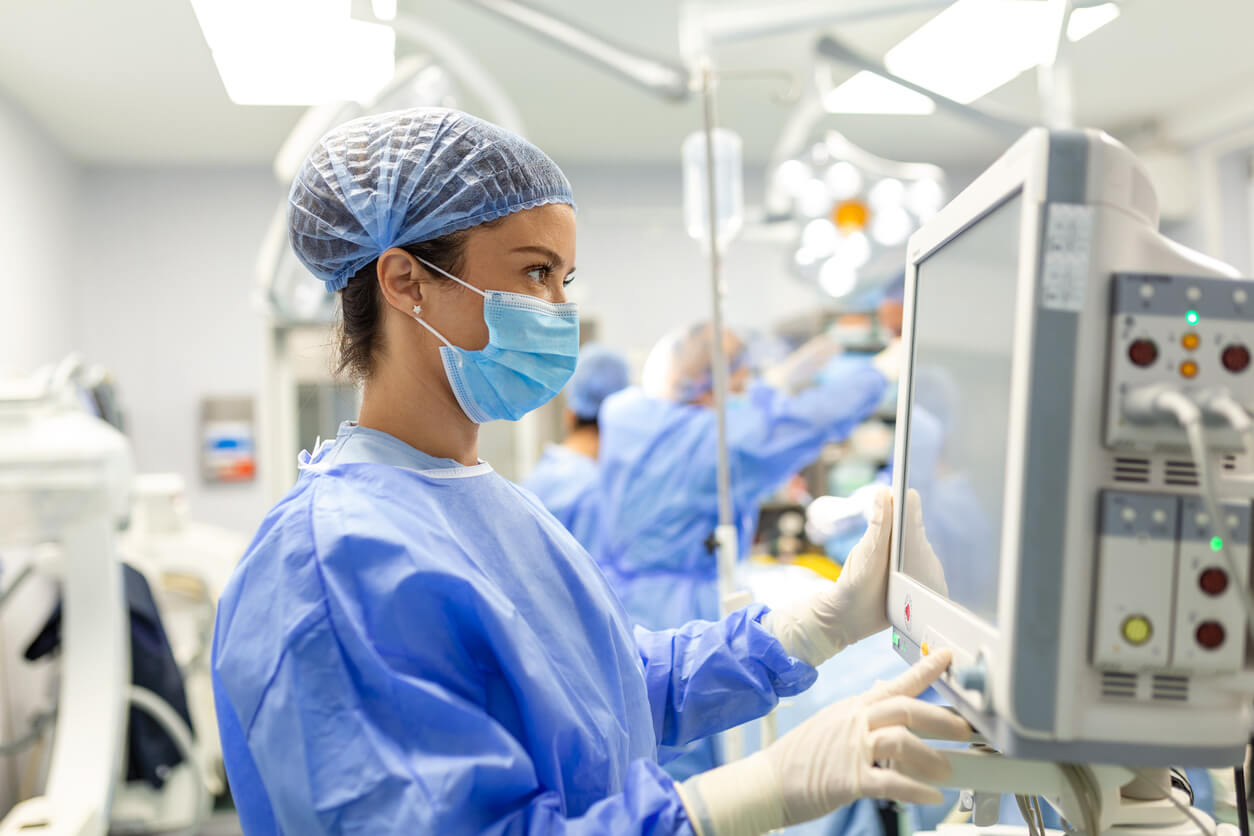
 5G will have major impacts on telehealth and health research. Telehealth is nothing new, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic pushed wide adoption of telehealth practices. With 5G, these practices will improve greatly. High speed, high quality video, along with VR, will allow clinicians to better diagnose and treat patients from a distance. More connected devices, including wearables, like smart bandages and smartwatches, and implanted devices, such as pacemakers, will collect and transmit massive amounts of patient data.
5G will have major impacts on telehealth and health research. Telehealth is nothing new, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic pushed wide adoption of telehealth practices. With 5G, these practices will improve greatly. High speed, high quality video, along with VR, will allow clinicians to better diagnose and treat patients from a distance. More connected devices, including wearables, like smart bandages and smartwatches, and implanted devices, such as pacemakers, will collect and transmit massive amounts of patient data.
The new ease at which we can collect and analyze health data will give way to new studies and research. Today, we study most health conditions in a laboratory, but 5G connected devices will allow us to study patients in their own homes. With large amounts of data being gathered and processed in real time, AI can be used to make predictions about people’s health, analyze patterns and discover new trends, and even recommend treatment.
5G will also have a huge impact on surgical practices. Autonomous robots are already being used for some surgical procedures. They reduce human error, can predict complications, and make surgery safer. However, current bandwidths cannot ensure that robots won’t lag or suffer from a slow network connection. So for now, surgeons mostly work with robots and other tools, which aid the surgery, but don’t fully control it. 5G could change that.
M2M communication could play just as large a role in healthcare as it will in manufacturing. In the future, we could see fully autonomous surgical procedures, which consist of monitors, IVs, and surgical robots, which all communicate as OR staff do today.
Preparing for 5G
 Most major cities in the US already have 5G networks in place, but our devices can’t access them. 5G uses a new frequency of radio waves, and your smartphone or connected device must be 5G enabled in order to access these frequencies. This means you can’t just switch your current smart phone or tablet to a 5G network, you need new hardware. This could be a challenge for the healthcare and industrial industries, where hardware is meant to last much longer than consumer devices. Even though 5G may not have an impact immediately, it’s smart to “future-proof” your technology. This means deploying computers and tablets with 5G capability.
Most major cities in the US already have 5G networks in place, but our devices can’t access them. 5G uses a new frequency of radio waves, and your smartphone or connected device must be 5G enabled in order to access these frequencies. This means you can’t just switch your current smart phone or tablet to a 5G network, you need new hardware. This could be a challenge for the healthcare and industrial industries, where hardware is meant to last much longer than consumer devices. Even though 5G may not have an impact immediately, it’s smart to “future-proof” your technology. This means deploying computers and tablets with 5G capability.
5G will revolutionize how we do business, access healthcare, produce goods, and how we communicate on a daily basis.
Learn about Teguar’s 12” Rugged Tablet with 5G, the first industrial-grade tablet to utilize 5G.
Sources:
https://www.broadbandsearch.net/blog/what-exactly-is-5g
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/future-factory-manufacturing-tech-trends/
https://www.gsma.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/The-5G-Guide_GSMA_2019_04_29_compressed.pdf
https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/backgrounders/Pages/5G-fifth-generation-of-mobile-technologies.aspx
https://www.pcmag.com/news/the-killer-app-for-5g-networks
https://rantcell.com/comparison-of-2g-3g-4g-5g.html