Edge Computing vs IoT: What is the Difference?

Edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) are two transformative technologies that have gained significant attention in the digital landscape. While they are closely related and often interconnected, they represent distinct concepts with unique characteristics and functionalities. Understanding the difference between edge computing and IoT is crucial for organizations and individuals seeking to harness the potential of these technologies effectively.
As we navigate the intricacies of this technological landscape, it becomes evident that both edge computing and IoT play pivotal roles in shaping the future of digital ecosystems. These technologies are not merely trends but rather catalysts for innovation, revolutionizing the way we process, analyze, and utilize data. Edge computing brings processing power closer to the source, enabling real-time insights, while IoT interconnects devices, creating a web of intelligent systems. Together, they form a dynamic synergy that has the potential to redefine industries, enhance efficiency, and unlock new possibilities for technological advancements. In this article, we will delve into the core aspects of edge computing and IoT, exploring their individual strengths and how their convergence opens doors to unprecedented opportunities in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
What is Edge Computing?
At its core, edge computing represents a departure from the traditional centralized model of data processing. In contrast to the dependence on a centralized cloud-based system, this approach underscores localized computation and storage near the data source. The primary goals are to reduce latency, optimize bandwidth, and enhance security and privacy.
Key Characteristics of Edge Computing
Proximity: The hallmark of edge computing is its proximity to the data source, minimizing the physical distance data must traverse. This localization ensures a swift and efficient processing cycle.
Low Latency: Immediate processing at the edge translates to low latency, a critical factor for applications demanding real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Decentralized Architecture: Unlike the centralized model, edge computing adopts a decentralized architecture. This means computing capabilities are distributed across various nodes rather than relying on a singular processing hub.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Reduced Latency: Edge computing’s ability to process data at the source minimizes the delay between data generation and processing. This is indispensable for applications requiring immediate responses, like autonomous vehicles navigating complex environments.
Bandwidth Optimization: By processing data locally, edge computing eases the strain on network bandwidth. This optimization proves especially valuable for applications dealing with substantial data volumes, ensuring efficient data flow.
Enhanced Security and Privacy: Localizing data processing enhances security by keeping sensitive information close to its source. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and provides a robust foundation for safeguarding critical information.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
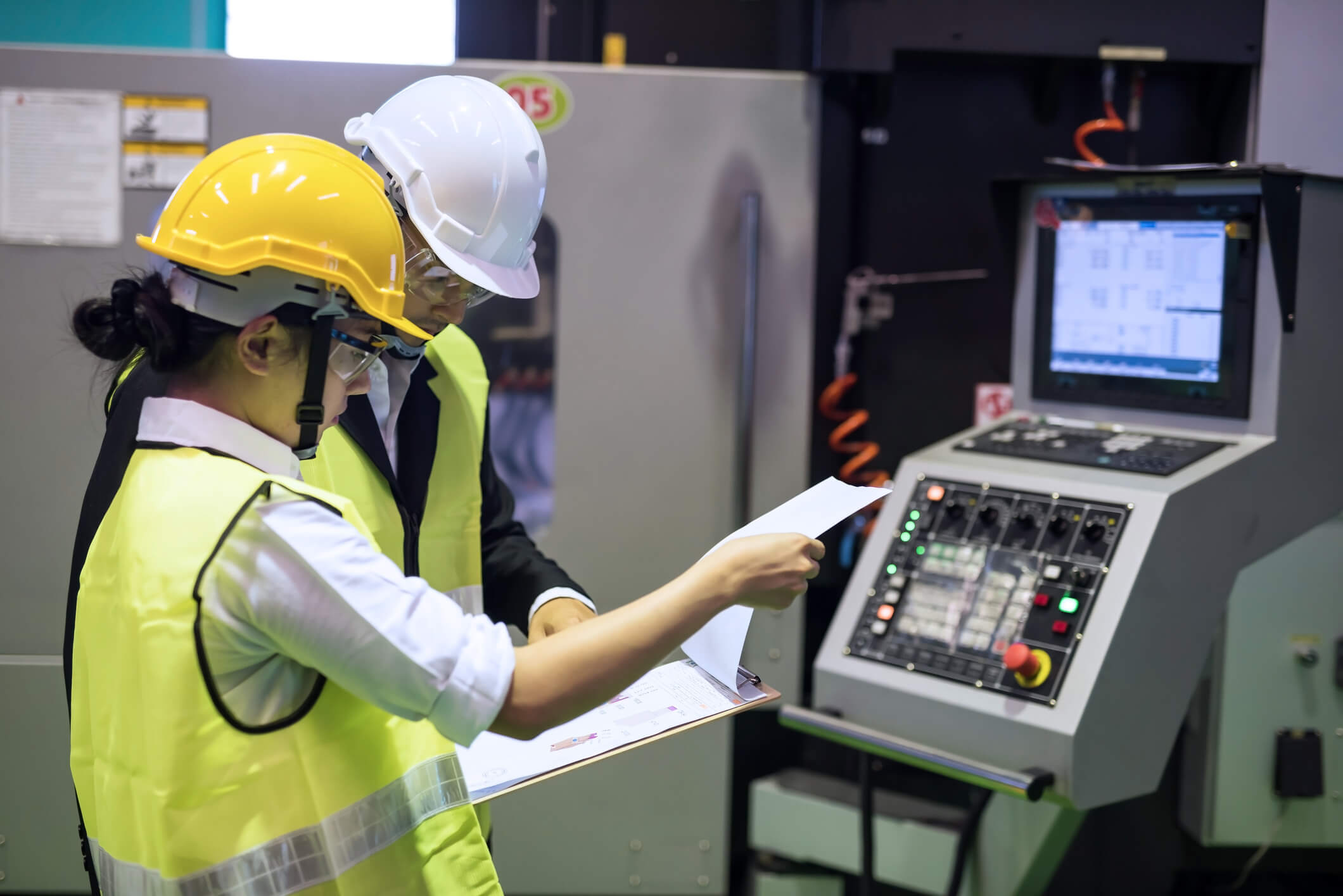
Smart Manufacturing: Edge computing facilitates real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, optimizing efficiency and minimizing downtime in industrial settings.

Smart Grids: In the energy sector, edge computing plays a pivotal role in optimizing grid management, allowing for rapid responses to fluctuations in demand and ensuring a stable energy supply.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to an intricate network of interconnected devices and systems capable of communicating and sharing data. Equipped with sensors and actuators, these devices enable a seamless exchange of information, marking a significant shift in how we perceive and interact with technology.
Key Characteristics of IoT
Interconnected Devices: IoT devices collaborate seamlessly, sharing data and executing tasks collectively to achieve overarching objectives.
Data Collection: Sensors embedded within IoT devices actively collect and transmit data, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the environment.
Automation: A defining feature of IoT is its automation capabilities, allowing devices to respond to predefined triggers, significantly reducing the need for manual intervention.
Benefits of IoT
Efficiency and Productivity: The automation and real-time monitoring facilitated by IoT devices enhance operational efficiency, reducing human intervention and minimizing errors in various industries.
Enhanced Decision-Making: IoT-generated data provides valuable insights, empowering decision-makers across industries to make informed choices based on real-time information.
Automation and Remote Control: The ability to remotely control devices is a key advantage of IoT, offering convenience and efficiency in tasks such as home automation and industrial processes.
Use Cases of IoT
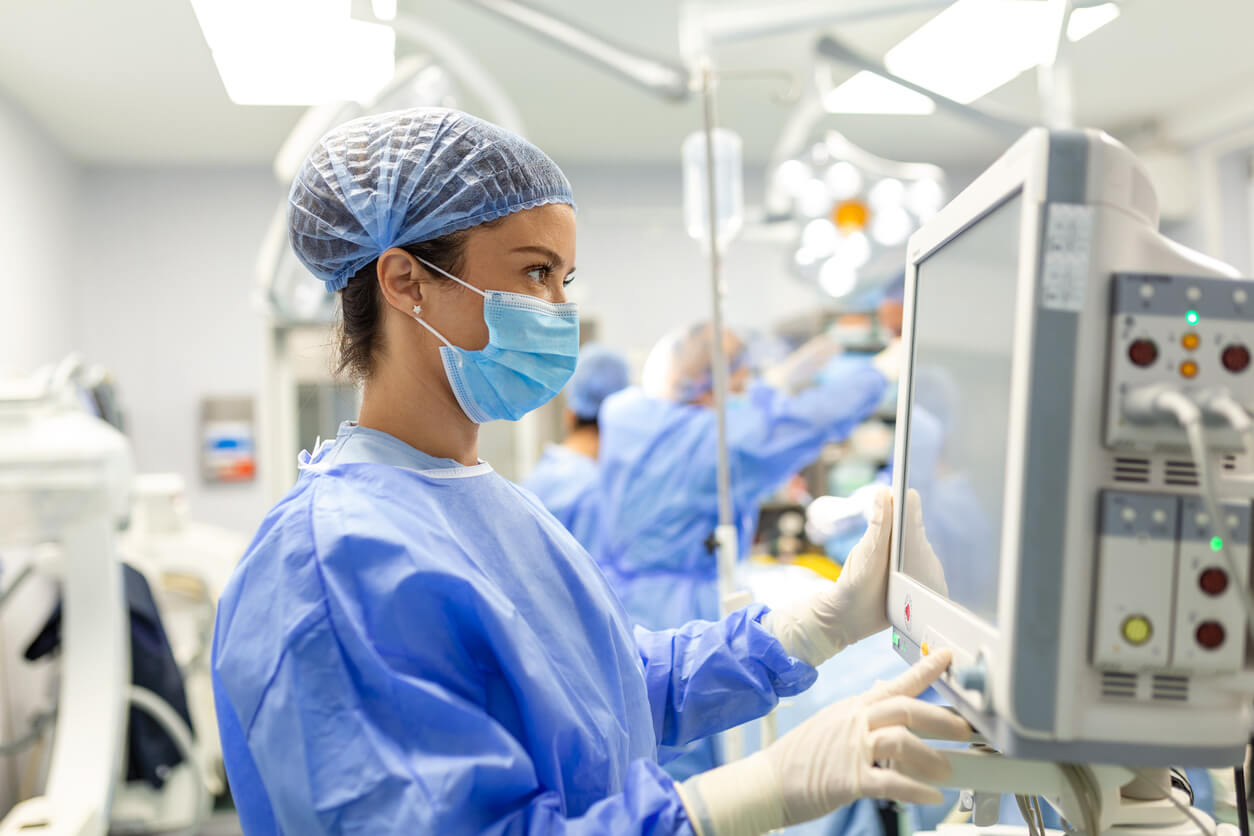
Healthcare Monitoring: Wearable devices and IoT-enabled healthcare systems provide real-time health monitoring, revolutionizing patient care through continuous data collection and analysis.

Supply Chain Management/Warehousing: In logistics and supply chain management, IoT optimizes inventory tracking and management, leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
The Differences Between Edge Computing and IoT
Data Processing and Storage
Edge Computing (EC): In edge computing, data processing and storage are localized, occurring near the data source.
IoT: In contrast, IoT relies on centralized or cloud-based processing and storage, involving a more centralized approach.
Network Architecture
EC: Edge computing embraces a decentralized and distributed architecture, distributing processing capabilities across various nodes.
IoT: IoT, on the other hand, relies on a centralized and hierarchical structure, where communication and data flow follow a more centralized path.
Real-Time Processing
EC: Edge computing ensures immediate, on-site processing, providing real-time insights and responses.
IoT: In the case of IoT, data aggregation and periodic processing are more common, introducing a slight delay in response times.
Scale and Scope
EC: Edge computing operates on a limited scale, with a localized scope tailored to specific environments.
IoT: IoT, in contrast, involves large-scale deployments with a global scope, connecting devices and systems on a broader scale.
Synergies and Convergence Between IoT and Edge Computing
Complementary Technologies
Edge computing and IoT are not mutually exclusive; rather, they complement each other. Edge computing addresses latency and bandwidth challenges associated with processing IoT-generated data.

Collaborative Use Cases
The collaboration between edge computing and IoT is evident in applications like smart cities, where edge devices process data locally, and IoT devices contribute to the broader network. Together, they form a cohesive ecosystem that maximizes efficiency and responsiveness.
Challenges and Considerations
While the synergy between edge computing and IoT is promising, challenges exist. Integration hurdles, security concerns, and the need for standardized protocols are key considerations when deploying solutions that leverage both technologies.
The Future of Synergy
The distinctions between edge computing and IoT are paramount for organizations and individuals seeking to harness the full potential of these technologies. Edge computing, with its localized processing and storage capabilities, is well-suited for applications demanding low latency and enhanced security. In contrast, IoT excels in interconnecting devices, automating processes, and providing valuable data insights.
The synergy between edge computing and IoT presents exciting opportunities for future technological advancements. Recognizing the collaborative potential of these technologies and addressing integration challenges are crucial steps for organizations aiming to stay at the forefront of innovation. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the combined power of edge computing and IoT will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of technology and its applications across various industries, offering unprecedented possibilities for efficiency, connectivity, and responsiveness.
About the Authors:
Emily Vrettos, Teguar's Digital Marketing Coordinator, merges her creativity with marketing skills to craft engaging content. When she isn’t writing, she loves to read, cook lots of different cuisines, and travel home to her family in New England.Previous Article
Panel PC vs. HMI: Choosing the Right Industrial Computing Solution