Faster Diagnoses, Smarter Decisions: Edge Computing’s Influence on Healthcare Analytics
The COVID-19 pandemic made it more apparent that the healthcare industry needed better ways to process and store all the data it produces. Enter edge computing, a transformative solution that promises to reshape healthcare analytics by processing data closer to its source.
The healthcare technology landscape has seen remarkable advancements, from digital health records to telemedicine. However, the key to improving patient outcomes is enhancing the speed and precision of medical decision-making.
In this article, we explore how the advent of edge computing offers a transformative solution that brings computation closer to data sources. Edge computing is revolutionizing healthcare analytics, improving diagnosis speed, and opening doors to predictive analytics, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
The Data-Driven Healthcare Revolution
Today, the healthcare industry is undergoing a significant data revolution. Patients are generating unprecedented digital health data thanks to telehealth, wearable devices, and patient portals. This influx of data has transformed the healthcare landscape, demanding greater attention to the proper management, storage, and security of patient information.
To ensure the integrity of this data, everyone involved in the ‘patient data pipeline,’ from the receptionist at the practice to the billing specialist handling payments, must be well-versed in data storage and security best practices. Healthcare administrators who oversee the entire data pipeline must take a proactive approach to data management and storage.
However, the vast volume and complexity of healthcare data present challenges for data administrators. This data encompasses electronic health records, medical images, remote monitoring data, and various other sources. Healthcare providers urgently require efficient data processing and analysis methods to transform this wealth of information into actionable insights.
Data administrators are increasingly turning to edge computing in healthcare due to its ability to process data closer to its source. With healthcare data’s growing volume and complexity, edge computing offers a solution that enhances data processing speed and real-time analysis, enabling healthcare providers to make quicker and more informed decisions. But how does edge computing work, exactly?
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing is gaining traction in healthcare as a new data-handling method. At its core, edge computing means processing data as close to where it’s generated as possible, which differs from the usual centralized approach. This shift brings many advantages, particularly in a healthcare landscape increasingly defined by the sheer volume and urgency of patient-generated data.
In a typical scenario, this tracker sends your heart rate data to a distant satellite for processing. The satellite then relays the results to your tracker to display on the screen. However, with edge computing, your tracker takes charge of this process, instantly measuring your heart rate and providing the result directly on your wrist. It’s like the difference between having a personal assistant and using Siri to schedule a meeting.
Edge devices, like these wearables, are vital to healthcare administrators. They’re the ones doing the work of storing and processing data. An edge device could be your fitness tracker, a smart thermometer, or even a particular sensor in a hospital room. Whatever their form, they collect and process data right where it’s happening, meaning you get current patient data at your fingertips.
Edge computing offers several noteworthy advantages in healthcare. Firstly, it bolsters patient data security by limiting it to a single device, minimizing potential vulnerabilities. Additionally, it expedites healthcare operations through real-time data analysis, empowering healthcare providers to diagnose and treat patients swiftly. This approach accelerates processes and elevates patient care by enabling timely interventions and personalized treatments.
Edge Computing’s Impact on Healthcare Analytics
By using edge computing, your healthcare business can stay ahead of the curve. Here are some practical ways edge computing can improve your analytics.
Proximity to Data Sources
One of the fundamental ways edge computing revolutionizes healthcare analytics is by bringing data processing closer to the source. By minimizing the physical distance between the data generated by healthcare devices and the computational resources, edge computing significantly reduces latency.
This reduction in delay means that critical data can be analyzed and acted upon almost instantaneously, a crucial advantage when your doctors need to make timely decisions. Whether it involves monitoring a patient’s vital signs or interpreting diagnostic images, edge computing’s proximity to data sources ensures that critical information is readily available, significantly boosting the speed and efficiency of healthcare processes.
Real-time Analytics
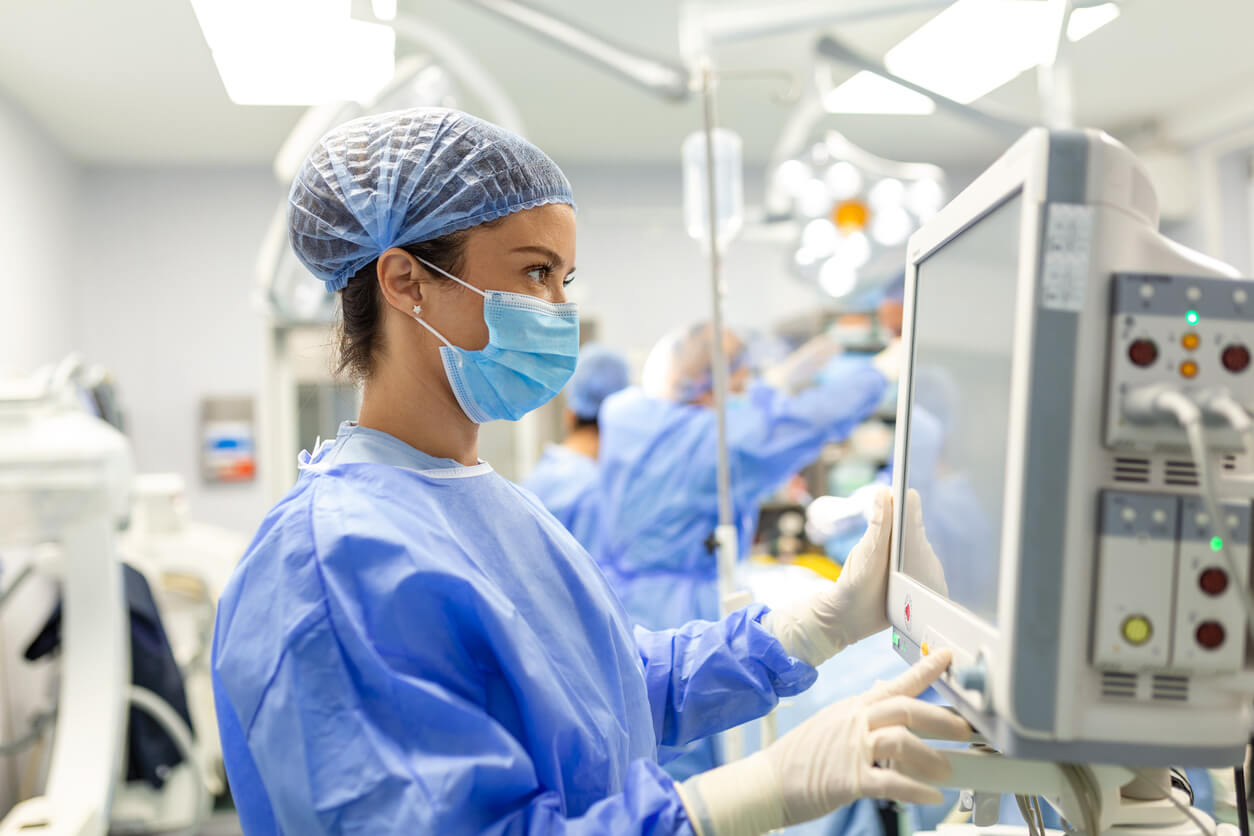
The capability of edge computing to enable real-time analytics represents a groundbreaking advancement in healthcare. Healthcare providers gain immediate insights into patient conditions and treatment effectiveness by processing data on-site.
For instance, wearable devices continuously analyze a patient’s physiological data and alert medical professionals to anomalies or emergencies as they occur. This responsiveness empowers healthcare teams to make swift, well-informed decisions, leading to faster diagnoses, more timely interventions, and improved patient outcomes.
Privacy and Security Considerations
While the advantages of edge computing in healthcare analytics are clear, it’s crucial to address privacy and security concerns. Storing and processing sensitive patient data on edge devices necessitates robust security measures to safeguard against breaches or unauthorized access. Healthcare organizations must adopt stringent data encryption, access controls, and secure communication protocols to protect patient information.
Moreover, compliance with healthcare data regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, remains a top priority to maintain patient privacy even in edge-based healthcare analytics. Balancing the benefits of real-time data processing with the imperative of data security is a critical challenge in realizing the full potential of edge computing in healthcare analytics.
Enhancing Diagnostics and Treatment Decisions
Case studies and practical applications of edge computing in healthcare have unveiled intriguing possibilities. Edge computing has the potential to address various challenges in the healthcare industry, ranging from improving connectivity in remote areas to enhancing patient engagement and enabling real-time diagnostics.
Consider a scenario where a wearable medical device continuously monitors a patient. With edge computing, this device can immediately detect any irregularities in the patient’s vital signs and transmit this critical information directly to the healthcare team. This instant communication allows for rapid responses, leading to earlier diagnoses and more timely interventions, potentially saving lives and reducing complications.

Furthermore, edge computing plays a pivotal role in predictive analytics. By analyzing historical patient data alongside real-time information from edge devices, predictive algorithms can forecast emerging health trends and pinpoint individuals at risk of specific conditions. By utilizing edge devices rather than traditional data sources, predictive algorithms can use the most up-to-date data and calculate potential patient health factors faster.
Finally, the impact of edge computing on healthcare extends to medical imaging. Instead of transmitting large medical images to centralized servers for processing, edge devices can locally analyze and enhance these images. This significantly reduces the time required to obtain critical insights from imaging, aiding in quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
Challenges of Edge Computing in Healthcare
As the healthcare sector increasingly adopts edge computing, it faces several practical challenges.
Integration
One key issue is making different types of edge devices integrate smoothly. These devices, such as medical sensors and wearables, often employ diverse technologies that do not inherently communicate with each other. Finding common ground and standards for data exchange is essential to fully benefit from edge computing. Healthcare organizations must work together and establish agreed-upon rules for sharing and using data.
Device Management
Another challenge is managing the growing number of edge devices as healthcare facilities expand. Ensuring these devices are working correctly, getting updates, and staying secure can become complicated. Device management software can ease this challenge, providing centralized control and monitoring of all connected edge devices. This system allows administrators to remotely configure, update, and troubleshoot devices, ensuring they operate correctly and securely.
Internet Connectivity
Another notable challenge of edge computing in healthcare is the need for reliable and high-speed network connectivity. Edge devices rely on seamless data transmission and instantaneous communication with centralized systems or other devices to function effectively. In healthcare, where split-second decisions can be a matter of life and death, any network downtime or latency can have serious consequences.
A single internet outage could impact your devices’ productivity and accuracy for days. Ensure your healthcare facility is equipped with high-speed internet, that your most crucial edge devices have backup storage systems, and that your facility is wholly prepared for an outage.
Processing Power
A significant challenge in implementing edge computing lies in finding computers that can effectively process substantial volumes of data. Edge devices, often characterized by their compact size and limited computational resources, may struggle to handle the increasing complexity and volume of data they collect. This is why you must look to specialized computer manufacturers for your edge computing needs.
As healthcare relies on timely and accurate data analysis, it is imperative to ensure that these edge devices possess the necessary computing power and storage capacity. Instead of looking into any device capable of edge computing, look into PCs explicitly designed for edge computing in medical spaces. Utilizing the proper hardware for your needs eliminates the chances of data loss, latency, and more.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
As someone in the medical field, you know how stringent the HIPAA rules are. The sensitivity and confidentiality of medical information mandate rigorous safeguards. When implementing a new edge computing system, ensure you are familiar with the safeguards you will need to protect patient data effectively. The minimum safeguards you need are data encryption, access controls, and a secure communication protocol.
While edge computing has a tangible benefit in giving real-time diagnostic data, healthcare workers must also ensure that data is adequately secured and that the patient consents to recording their data. Healthcare providers must adopt transparent policies regarding data collection and usage, ensuring that patients are well-informed and have a say in utilizing their data.
Ethical considerations in healthcare edge computing extend beyond data privacy and consent; they also encompass data bias and fairness within AI algorithms, primarily when employed in decision-making. When AI algorithms analyze patient data, they rely on historical information to make predictions or recommendations. However, these historical datasets can carry biases that may reflect past healthcare access, treatment, or outcome disparities. AI algorithms can perpetuate these biases if not correctly addressed, leading to unequal healthcare outcomes for specific patient groups.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Edge-Driven Healthcare Analytics
While still in its early stages, edge computing holds immense growth potential in the years to come. As patient data volumes continue to surge, edge computing solutions will play an increasingly vital role in managing and processing this information and facilitating comprehensive patient care.
The future of healthcare will be defined by a shift toward a patient-centric approach enabled by personalized edge analytics. Data from wearable devices and edge sensors will offer deeper insights into individual patient health and behaviors. This will empower healthcare professionals to tailor treatments and interventions to each patient’s needs, resulting in more effective care, better patient outcomes, and increased patient engagement.
Moreover, significant advancements in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring are on the horizon, all driven by edge computing. High-quality video consultations are poised to become the standard in telehealth, enhancing the patient experience and expanding access to care. The capacity of edge devices to collect and analyze patient data will bolster remote monitoring of chronic conditions, allowing healthcare providers to intervene promptly when necessary.

Finally, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will continue to be integral to edge computing, supporting advanced data analysis, predictive modeling, and precision clinical decision-making. As AI and ML technologies mature, they will adeptly process and interpret large volumes of patient data at the edge, ultimately elevating the quality and customization of healthcare interventions.
The influence of edge computing on healthcare analytics is undeniably profound. It has ushered in a new era, expanding the horizons of what’s achievable in healthcare by leaps and bounds. The ability to process data closer to its source has not only accelerated diagnoses, it has also enabled more efficient data analysis, equipping medical professionals with the necessary tools to make prompt, well-informed decisions.
As a leader in today’s medical computing landscape, we create medical computers that provide powerful support to the healthcare industry. Ensure you’re using the most powerful and dependable tech available by choosing Teguar’s advanced medical computing solutions today.